
Pilots
The partners of PIISA believe that piloting and demonstrating is the key to engagement and
continuous learning.
That is why we, in the PIISA project, will, via five pilots, develop innovative concepts, advanced
products and services that aim to enable co-creation with stakeholders and potential users. Each
pilot will be made up of three parts, or Loops as they are called in PIISA.
The following themes will be explored in the pilots:
Pilot 1 - Green Roof Insurances,
Pilot 2 - Addressing soil stability risks for home owner
insurance holders,
Pilot 3 - Insurance Services for Agriculture,
Pilot 4 - Forest Insurances against selected biotic and
abiotic risks
Pilot 5 - Wildfire insurance enhancing adaptive actions.
Description of PIISA Pilots
PILOT 1: Green roof insurances
Pilot lead: IVM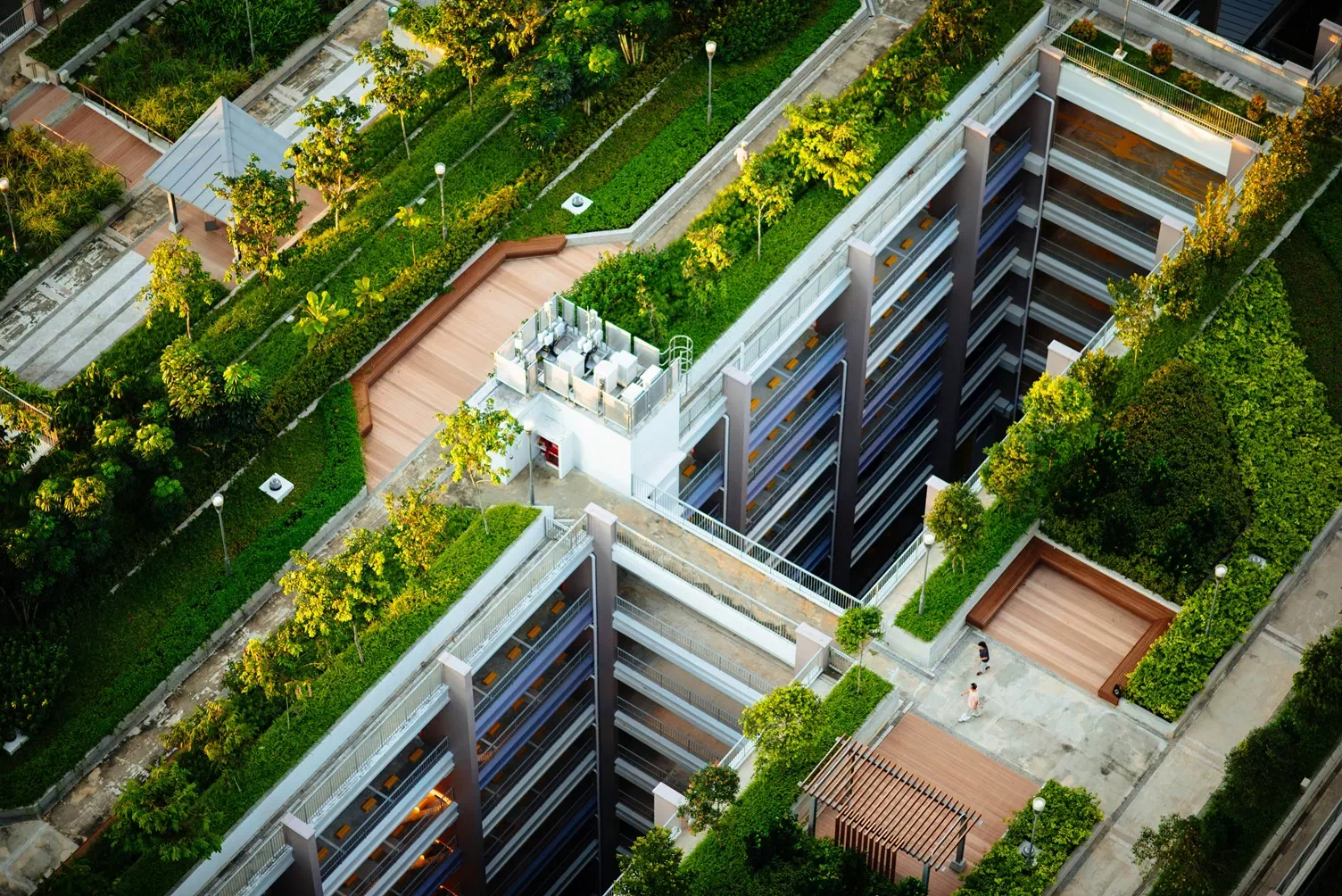
In this pilot, we study how insurance can stimulate the adoption of urban nature-based solutions, specifically green roofs. The overarching goal is to develop a European business model for insurance that promotes nature-based solutions. The implementation of green roofs is increasing, but still scarce, even though they provide a range of aesthetic, biodiversity, and recreational benefits in addition to various climate change adaptation and mitigation benefits, such as water management or insulation.
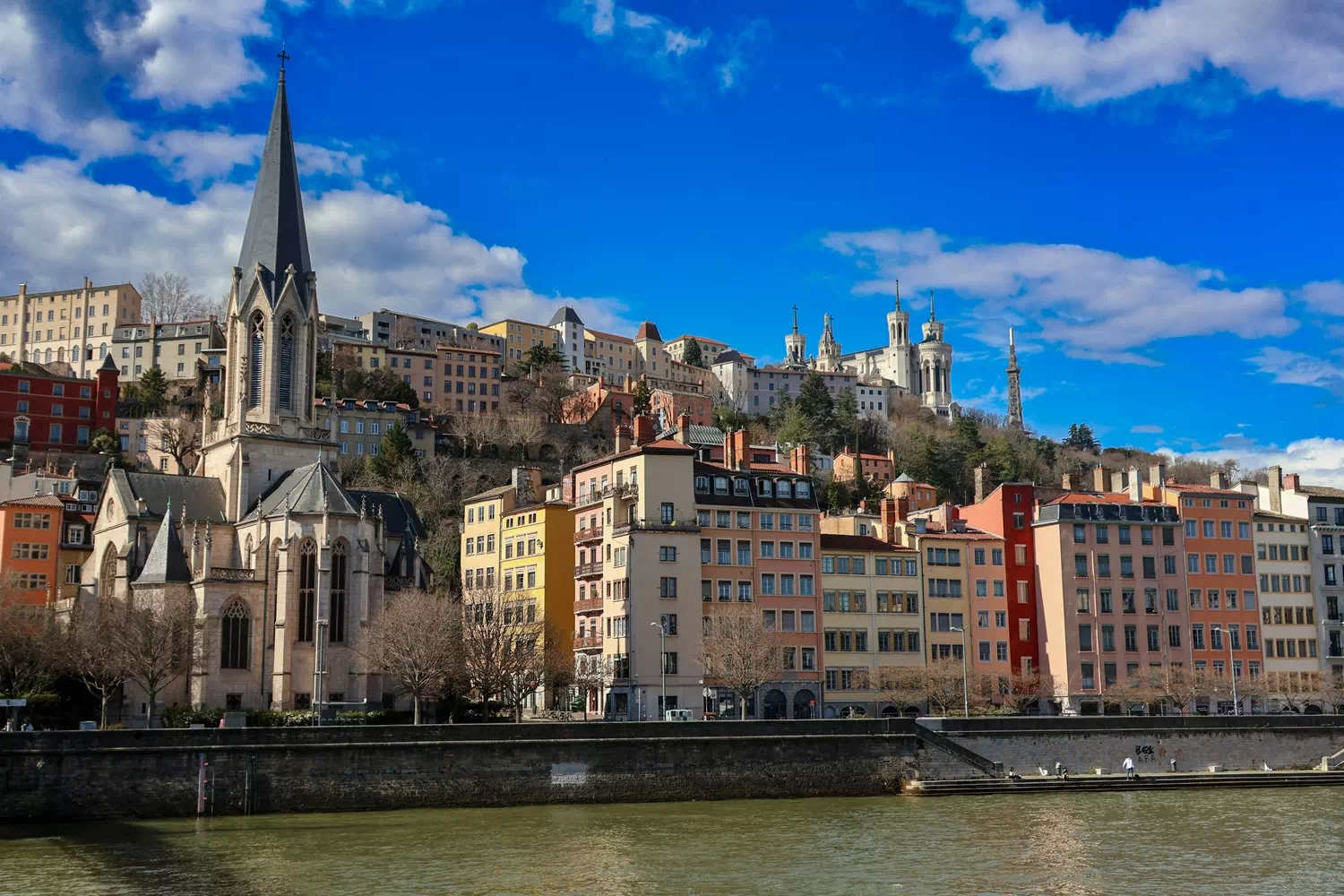
PILOT 2: Addressing soil stability risks for homeowner insurance holders
Pilot lead: Sustainable Finance ObservatoryThis pilot addresses homeowners and the risks associated with clay soil shrinkage and swelling. This phenomenon poses a substantial threat for homeowners as it has the potential to destabilise buildings and their foundations, causing structural damage - even beyond repair. The risk is increasing rapidly due to climate change, and it can potentially lead to large financial losses for homeowners where there are gaps in insurance cover. Our goal is to create an online dashboard that educates and empowers homeowners to manage their financial risks effectively from gaps in insurance cover.

PILOT 3: Insurance services for agriculture
Pilot lead: BSC CNS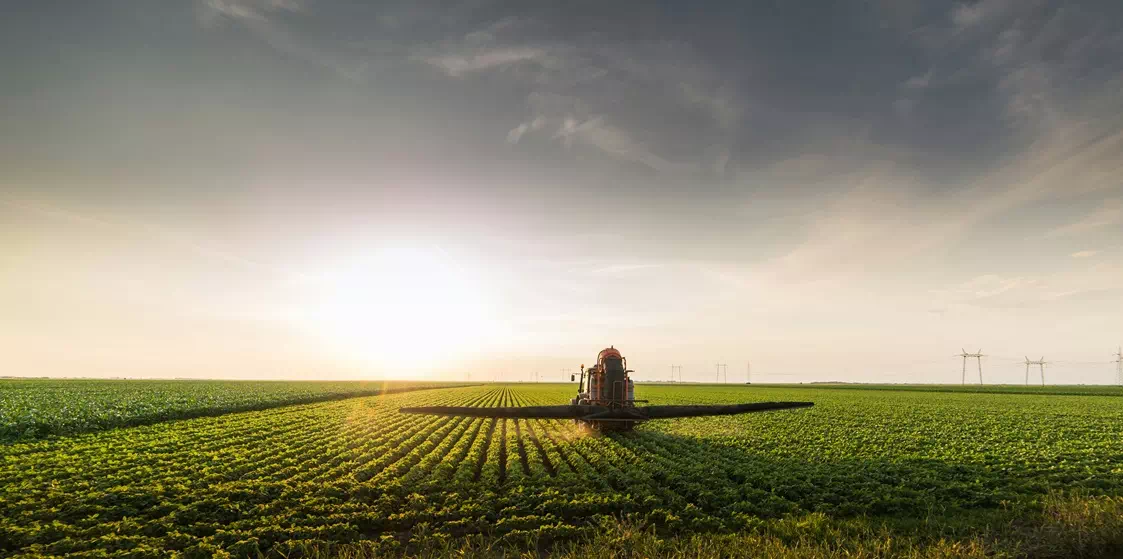
This pilot aims to co-develop a demand-driven, index-based insurance (IbI, also often called parametric insurance) solution that meets farmers' needs while ensuring viability for insurance providers. Collaborating with a farmer association in the Mediterranean region, we will understand local needs to develop tools that demonstrate the potential application of IbI in the agricultural sector. Additionally, we will support insurers in designing IbI products, particularly in the context of the Boreal region, by providing indicators related to weather phenomena that impact crop production. The pilot will further explore the potential for scaling these solutions across the EU.
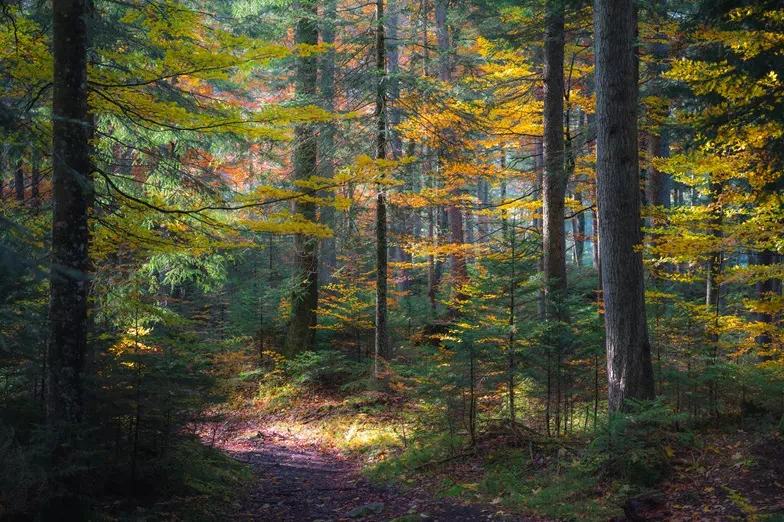
PILOT 4: Forest Insurances against selected biotic and abiotic risks
Pilot lead: AXA ClimateInsurance is a risk transfer solution which can compensate the financial losses of forest stakeholders following climate disasters, while encouraging landowners or forest managers to invest in risk reduction and adaptation measures. This pilot aims to actively engage forest owners and other key stakeholders in exploring existing forest insurance products and designing new innovative insurance covers that would also consider evolving climate risks and potential adaptation measures undertaken by the client.

PILOT 5: Wildfire Insurance Enhancing Adaptive Actions
Pilot lead: AXA Climate
Due to increased drought events, wildfires are increasing both in Europe and worldwide. Climate conditions, ignition triggers, and vegetation covers are the key drivers of wildfire propagation and intensity. To reduce vulnerability to fires, it is crucial to address how insurance mechanisms can promote adaptation measures at different levels. Thus, the purpose of this pilot is to develop innovative wildfire forest insurance to incentivise adaptation measures at household and forest association levels.
What do the first innovation rounds tell us?
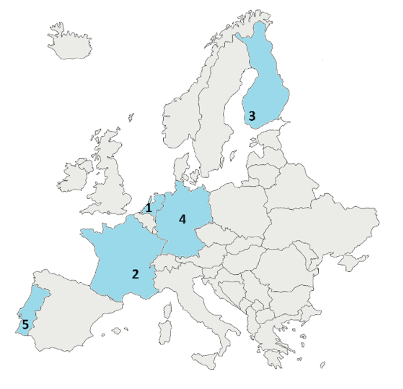
The first innovation rounds of the PIISA pilots are designed to cover different European biogeographical regions: Atlantic (Netherlands, pilot 1), Continental (France, pilot 2 and Germany, pilot 4), Boreal (Finland, pilot 3) and Mediterranean (Portugal, pilot 5).
- According to Risk Data Hub’s vulnerability index (European Commission Disaster Risk Management Knowledge Centre 2022*), the vulnerability indices of the first pilot countries are:
- Pilot 1 Amsterdam, Netherlands: 4 - 5
- Pilot 2 Lyon, France: 4 - 5
- Pilot 3 Finland: 2,5 - 4
- Pilot 4 Germany: 4 - 5
- Pilot 5 Central Portugal: 5 - 6
Pilot 1 starts in the Netherlands. The cities in Central Europe are densely built and populated, so there is a need for solutions that address heatwaves and droughts in such areas. Heatwaves are getting more frequent, longer, and hotter in Europe leading to droughts as well as the precipitation patterns are changing, with downpours and other precipitation extremes increasing in magnitude. (European Environment Agency 2024**).
In France, the issue of clay soil shrinkage and swelling is connected to more severe droughts and more volatile heavy rainfall. During longer droughts clay soil will dry and contract whereas during heavy rainfall significant saturation can cause swelling which can lead to property damage. The city of Lyon, where the pilot 2 starts, is vulnerable to this risk and the risk is expected to grow as climate change increases.
The vulnerability index in Finland is relatively low compared to other regions in Europe. According to the European Climate Risk Assessment (2024) the main climate risks in European agriculture are reductions in crop and livestock production from changing growing conditions and extreme weather events. However, the farmers In Finland are not very well prepared for all future risks, for example droughts, as there are no irrigation systems widely in place.
Forestry is an important industry in Germany. According to the European Climate Risk Assessment (2024), it is projected that climate change will increasingly affect the functioning and productivity of forests in all climate scenarios. The first innovation round of pilot 3 considers climate risks such as forest fire, drought, and pest outbreaks.
The pilot 5 starts in Portugal where the vulnerability index is the highest. The effects of climate change will affect Southern Europe heavily. Above average temperatures and drought conditions have already led to elevated risk of wildfires in the area. According to the European Climate Risk Assessment (2024), Southern Europe will experience extensive wildfires each year in the near future (2021 - 2040) and in the longer term the fires can be more frequent, intense and severe as the climate crisis progresses.
*) European Commission Disaster Risk Management Knowledge Centre. (2022). Risk Data Hub Vulnerability Dashboard. https://drmkc.jrc.ec.europa.eu/risk-data-hub#/dashboardvulnerability
**) European Environment Agency. (2024). European Climate Risk Assessment. EEA Report 01/2024.